In today's digital age, laser printers have become an essential tool for both personal and professional use. Understanding how laser printers function can help users optimize their printing experience and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. In this article, we will delve into the intricate workings of laser printers, exploring the technology behind them and shedding light on their key components and processes.
- The Laser Printing Process:
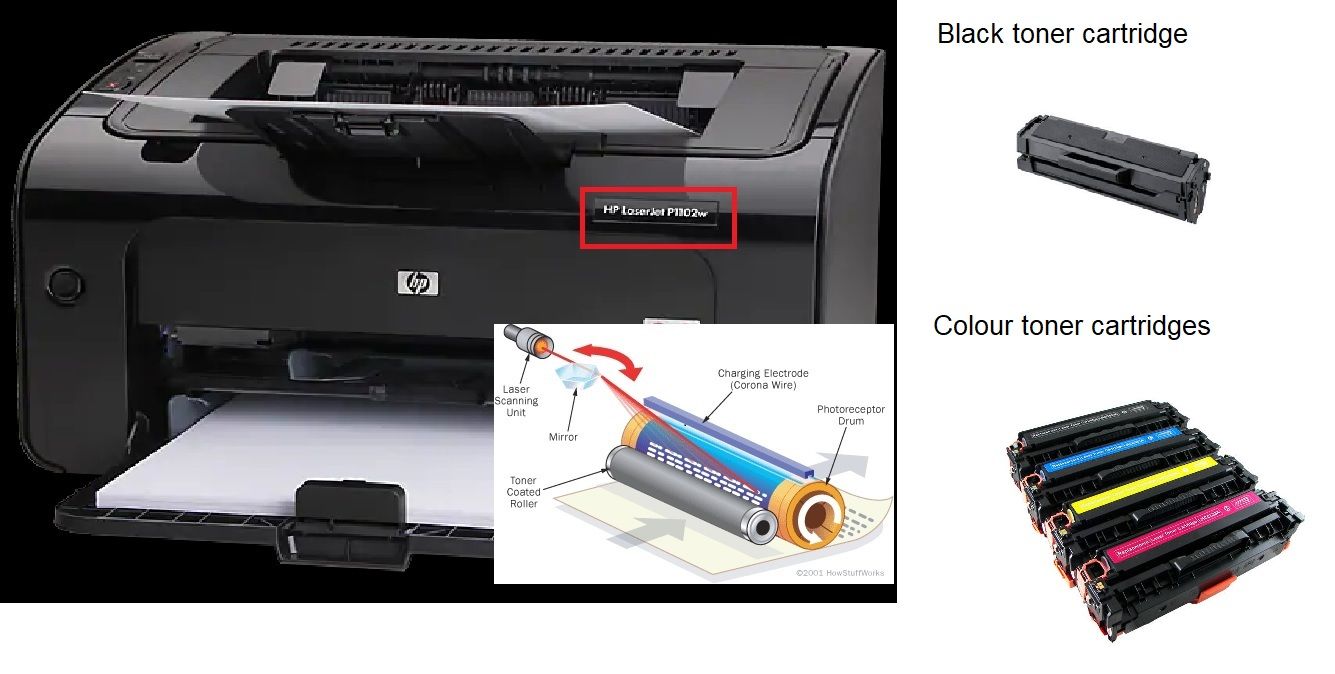
The laser printing process involves several steps that work together seamlessly to produce high-quality prints. It begins with the creation of a digital image, which is then translated into a series of electrical signals. These signals control the laser beam's movement, allowing it to selectively charge specific areas on a photosensitive drum. - The Photosensitive Drum:
At the heart of a laser printer lies the photosensitive drum, a crucial component responsible for capturing and transferring the image onto paper. Made of a light-sensitive material, the drum is initially given a positive charge. As the laser beam scans across the drum, it selectively discharges the charged areas, forming an electrostatic image. - Toner Cartridge and Electrostatic Image Transfer:
The next step involves the toner cartridge, which contains fine particles of powdered ink. The toner is negatively charged, allowing it to be attracted to the positively charged areas on the drum, effectively transferring the image onto the drum's surface. From there, the paper is introduced into the printing process. - Fusing the Image:
Once the toner has been transferred onto the paper, it needs to be permanently fixed. This is achieved through a process called fusing, where heat and pressure are applied to melt the toner particles and bond them to the paper fibers. The fuser unit, consisting of heated rollers, ensures that the toner is securely fused onto the paper, resulting in durable and smudge-resistant prints. - Cleaning and Maintenance:
To maintain optimal printing performance, laser printers incorporate various cleaning mechanisms. These include a cleaning blade or roller, which removes any excess toner from the drum after each print cycle, and a waste toner container, where the residual toner is collected. Regular maintenance, such as replacing consumables and cleaning the printer's interior, is essential for prolonging the printer's lifespan and ensuring consistent print quality.
Conclusion:
Understanding how laser printers function provides valuable insights into their inner workings and enables users to make informed decisions when it comes to printer selection, troubleshooting, and maintenance. By grasping the intricacies of the laser printing process, users can optimize their printing experience, achieve superior print quality, and extend the lifespan of their laser printers.